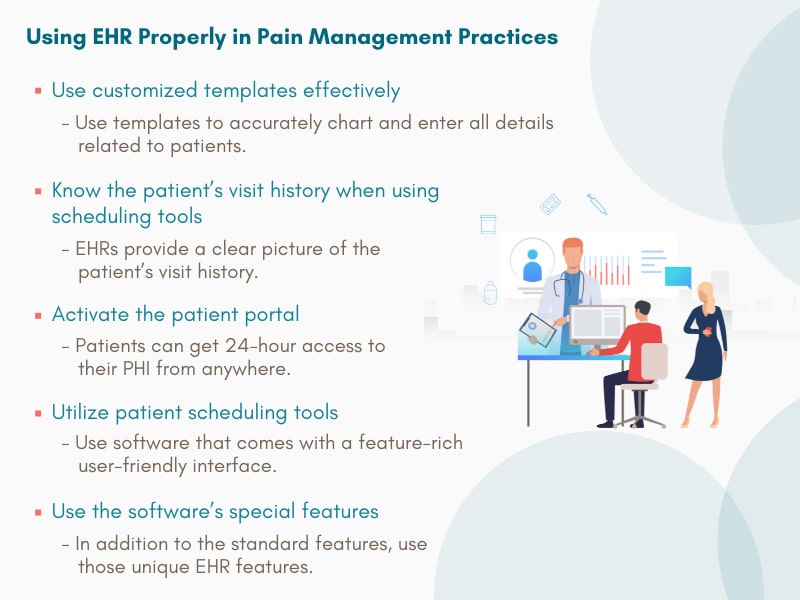
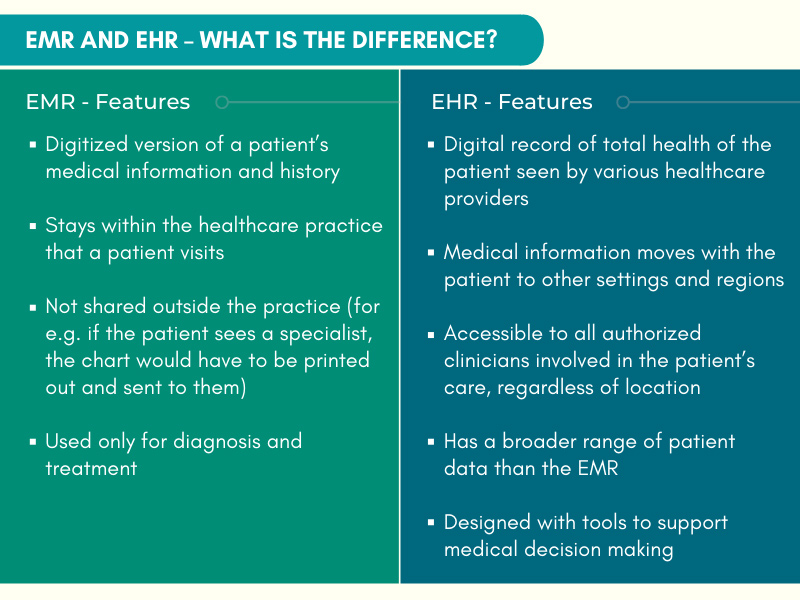
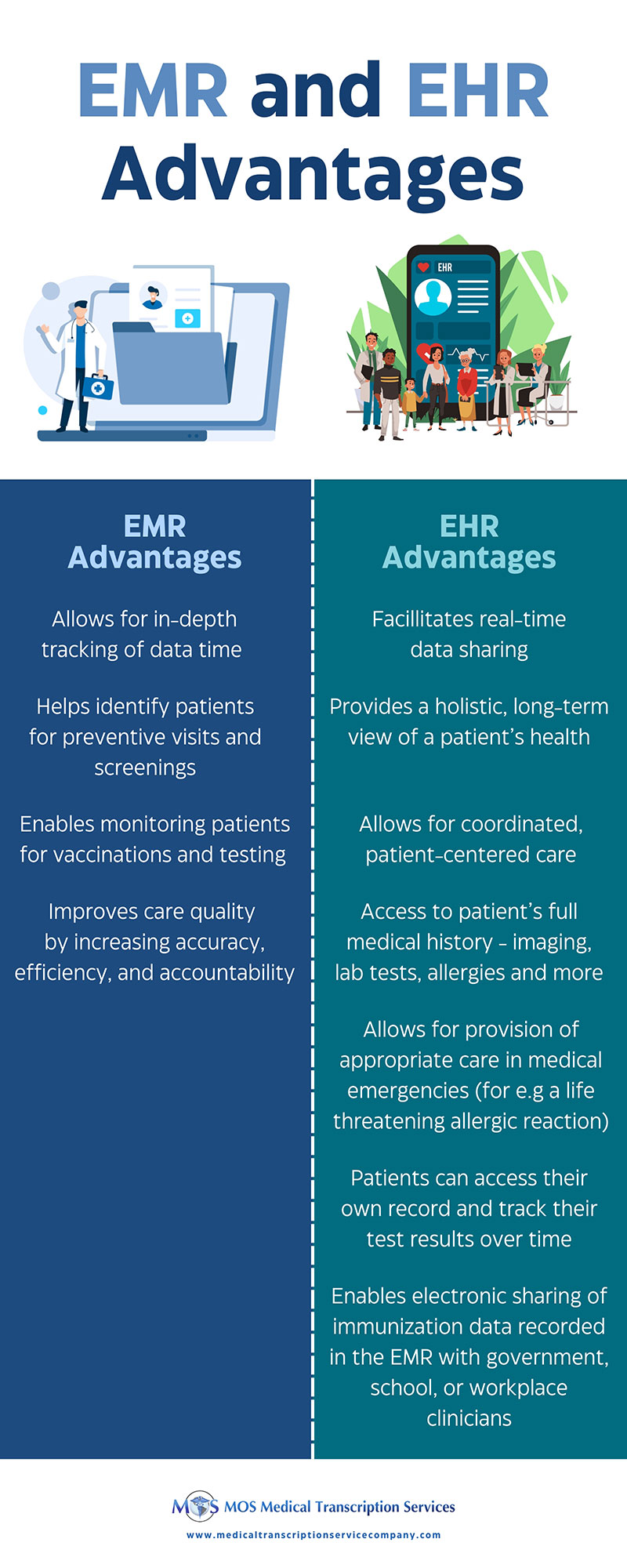
Open notes enable patients to view their clinicians’ notes on patient portals. Sharing notes benefits both patients and clinicians. These shared visit notes were created almost a decade ago by OpenNotes with the aim to improve the patient experience by empowering patients and families, better informing patient caregivers, and improving the quality and safety of patient care. The movement expanded, allowing millions of patients across the country to view their clinical notes. The 21st Century Cures Act mandate that became effective April 5, 2021, requires open patient access to clinical notes as part of its information blocking prohibition. The mandate covers eight types of clinical notes that medical transcription companies help healthcare providers create:
1. Consultation
2. Discharge summary
3. Procedure notes
4. Progress notes
5. History and Physical
6. Imaging narratives
7. Laboratory report narratives
8. Pathology report narratives
According to the OpenNotes organization, more than 50 million patients could access their clinical notes by the end of 2020. Studies of open notes have found that the strategy is indeed beneficial for patient. A May 2021 Journal of General Internal Medicine study reported that 50 percent of clinicians who started offering open clinical notes found that their patients took better care of themselves when given access. About 75% of providers noted better patient empowerment.
In a March 2020 public statement announcing the final information blocking rule, then-HHS Secretary Alex M. Azar said, “These rules are the start of a new chapter in how patients experience American healthcare, opening up countless new opportunities for them to improve their own health, find the providers that meet their needs, and drive quality through greater coordination.”
However, with the Cures Act mandate, clinicians will need to balance clinical documentation with a good patient experience. This means they will need to make patient notes more “patient-friendly, more understandable and more appropriately or compassionately worded”, says Steven Lane, MD, MPH, FAAFP, FAMIA, a primary care physician and Sutter Health’s clinical informatics director for privacy, information security, and interoperability (www.fortherecordmag.com).
Writing Good Patient Notes – Key Considerations
Focusing on the following aspects is critical to write good patient notes:
- Accuracy: Accuracy is vital. The physician should ensure documentation that is consistent, concise, and complete and captures the patient’s story correctly, so that both the patient and other healthcare providers can read and understand it. Patient care and safety would be compromised if treatment is based on inaccurate information in the chart. According to OpenNotes, when patients review their notes, accuracy improves as they become an extra set of eyes on the information and sometimes find issues that require correcting.
- Patient-friendly: Physicians will have to work on making notes understandable for the patient. Also, as patients will be reading their clinical notes, providers should take care to avoid any verbiage or phrases that can seem offensive or judgemental to patients. According to a recent study on clinical notes published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, words like “incorrect,” “obese,” “wrong,” “anxious,” “depressed,” “inaccurate,” or “elderly” came up quite often as unfavorable to patients (PatientEngagementHIT).
In its Steps Forward Module, the American Medical Association (AMA) notes that while providers don’t need to make any ‘dramatic changes’ in their style of writing notes, a recent OpenNotes follow-up survey reported that some said that they adjusted documentation to:- Avoid language that might be perceived as critical of the patient.
- Remove terms such as “non-compliant,” “patient denies,” and “patient refuses.”
- Change how they document sensitive clinical, mental health, or social information.
When writing open notes, clinicians should focus on:
- Being positive and supportive.
- Including only things discussed with the patient during that visit.
- Not including wording that could be interpreted by the patient as labeling or judgmental. For e.g., instead of “patient is obese,” say “Patient has BMI >30.” Don’t write “Patient refuses to take his medications,” instead note that the “Patient has been non-adherent to medications due to [provide a reason].”
- Minimizing the use of medical jargon, acronyms, and abbreviations to avoid anything that may be perceived as offensive.
- Capture pertinent information for coding and clinical documentation improvement (CDI): The medical record is the source document for coding and reporting diagnoses and procedures. The goal of CDI is to improve the clinical note, which contains information captured during the visit such as present illness, data measured and recorded, examination observations, an assessment, a definitive diagnosis, and a care management plan. Documented clinical notes should capture all the information required for coding and billing. Clinical documentation impacts the entire revenue cycle. Improper documentation of medical notes will lead to inaccurate coding, affecting billing and financial management, and care quality. While providing open notes that are useful to the patient, clinicians must ensure precise documentation that supports the service/supply billed. This will promote accurate coding and billing, which can lead to correct and timely reimbursements for the healthcare provider.
- Consider practice-specific needs/concerns: The AMA says that when sharing patient notes, practices need to be ready to handle specific concerns such as:
- whether notes created prior to open notes implementation will be shared
- educating patients on registering in the patient portal and where to find their notes
- how to answer patients’ questions on notes and correct any errors they find
- how to handle sensitive topics like adolescent health, mental health, etc,
To successfully implement open notes, physicians should discuss the importance of transparency with their team and educate them on the benefits of open notes while addressing legal requirements. They should also prepare patients and their care partners using strategies like sending emails introducing the initiative, posting explanatory documents on their website, and promoting the adoption of open notes via social media channels.
Role of Medical Transcription Services
With the call for increased transparency in healthcare, open notes are here to stay. On its website, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) notes that enabling patients to read and amend their chart enhanced opportunities to:
- Identify serious inaccuracies and avoid medical errors
- Share notes with other clinicians
- Reinforce the clinician’s findings and recommendations discussed at a visit
- Clarify something the clinician said or did at the visit
- Improve patients’ insights into clinicians’ decision-making
- Help patients gradually accept and adjust to some diagnoses
- Motivate patients to comply with prescribed behavioral modifications
- Help patients prepare for office visits
- Dismiss unconfirmed worries about clinician findings or thoughts
- Involve family and other caregivers in the patient’s care
Open notes would be able to successfully meet these objectives only if they are error-free.
Accuracy is paramount, says Association for Healthcare Documentation Integrity President-Elect Stacy Lehto, CHDS, AHDI-F (For the Record Magazine). Focusing on patient friendliness at the expense of accuracy and completeness could lead even the best provider or facility to lose all credibility, says Lehto.
Studies report that as much as 10% of patients find errors in their records, and they consider 25% of these mistakes as serious. Importantly, 25% of physicians who have been offering open notes for more than a year say that patients have found errors that the physicians themselves felt were serious.
A JAMA study published in 2020 that looked into the frequency and types of errors identified by patients who read open ambulatory visit notes found that a specific error in current or past diagnoses was most common (27.5%), followed by incorrect medical history (23.9%), medications or allergies (14.0%), and tests, procedures, or results (8.4%). Up to 6.5% notes were found to be written on the wrong patient.
Many errors occur when physicians are overburdened with documentation. According to the researchers, overburdened practitioners may import inaccurate medication lists, and transmit other flawed information electronically by copying and pasting older parts of the record, or enter incorrect examination findings. Among primary care physicians sharing notes with patients, 26% expected that patients would find nontrivial errors. As practitioners use EHR data for decision-making, such errors could lead to medication errors, wasteful duplication, redundant or incorrect treatment, and delayed diagnoses.
As clinicians focus on best practices for sharing clinical notes with patients, medical transcription outsourcing can play an important role making it work by ensuring accurate documentation. Family practice medical transcription service providers can ensure accurate documentation of consultation, procedure and progress notes, discharge summary, history and physical, and imaging report, laboratory report and pathology report narratives. They have experienced medical transcriptionists and quality assurance professionals on board who can ensure error-free documentation in the electronic health records (EHR), thereby reducing the likelihood of errors in open notes.
View our infographic on Key Tips To Write Open Clinical Notes [INFOGRAPHIC]