Table of Contents
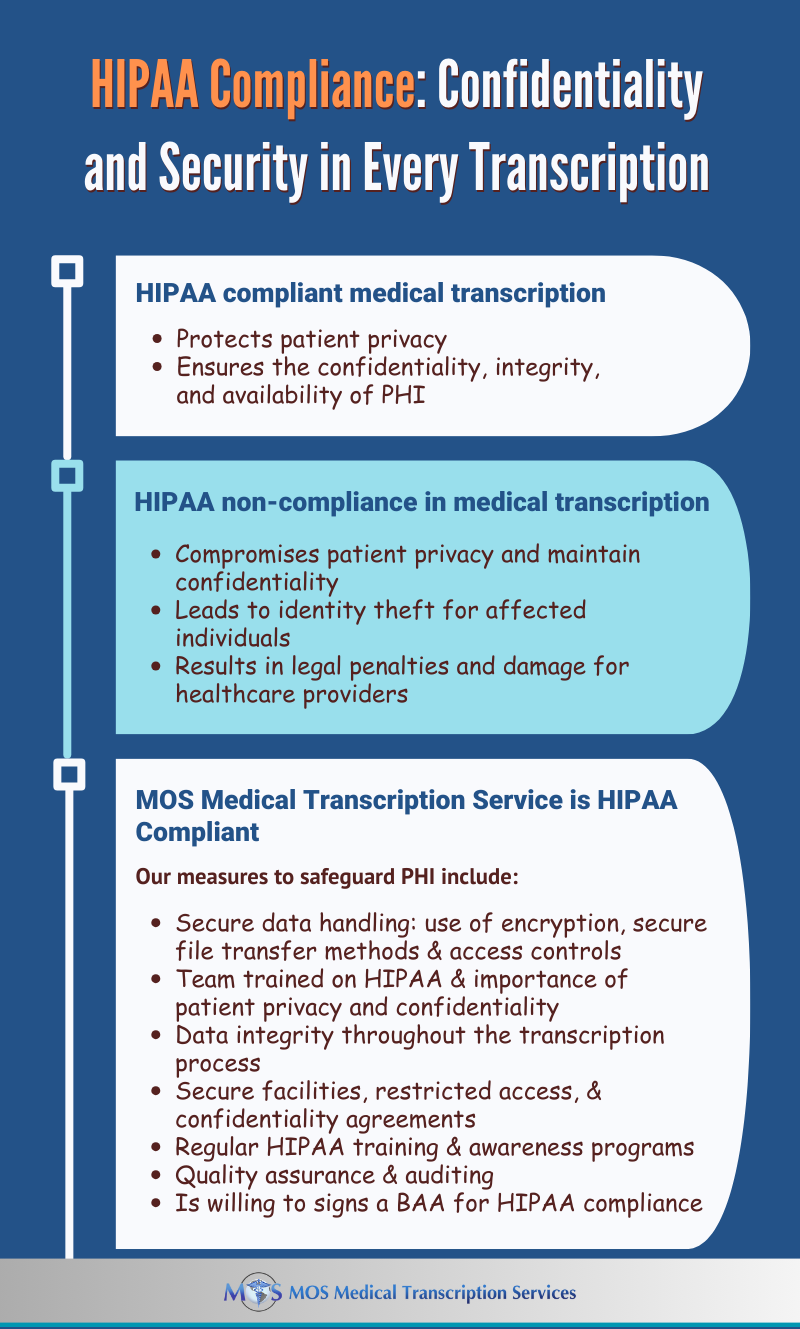
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establishes the standard for protecting sensitive patient data or the confidential use of protected health information (PHI). “Covered entities” or “business associates” that handle PHI are required to be HIPAA-compliant. Covered entities refer to health plans, health care clearinghouses, and health care providers. Business associates mean all organizations or individuals who act as a vendor or subcontractor with access to PHI. A US based Medical transcription company comes under the business associate category and can be held liable for PHI exposure. That’s why you need to strictly enforce HIPAA transcription confidentiality regulations.
What HIPAA Compliance Means for a Medical Transcription Company
HSS.gov defines a “business associate” as a person or entity that performs certain functions or activities that involve the use or disclosure of protected health information on behalf of, or provides services to, a covered entity. As a business associate, a medical transcription company has to provide a written assurance or sign a contract with the covered entity or healthcare provider that it will appropriately safeguard patient identifying information. This means that the company must have the necessary infrastructure and regulations in place for securing and maintaining the confidentiality of PHI.
The HIPAA regulations that apply to a medical transcription company are as follows:
- The company must ensure that the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all PHI handled or transmitted is preserved.
- It should not use or further disclose the information other than as permitted or required by the contract or as required by law.
- It should implement appropriate safeguards to prevent reasonably anticipated but unauthorized use or disclosure of the information, including implementing requirements of the HIPAA Security Rule with regard to PHI.
- The company must protect PHI it handles against reasonably anticipated threats to the security or integrity of the information.
- It should ensure workplace compliance.
|
In 2022, an average of 1.94 healthcare data breaches of 500 or more records were reported each day (HIPAA Journal) |
Measures for HIPAA Compliance
A HIPAA compliant medical transcription company will have proper measures in place to ensure security, health care compliance and privacy of PHI. Achieving HIPAA transcription compliance means your company has to maintain and implement effective written policies and procedures as well as implement administrative, physical and technical safeguards and controls to protect PHI:
- Physical and Technical Safeguards
HIPAA compliant medical transcription means have the necessary physical and technical safeguards in place to protect PHI. This includes:
- Measures to restrict physical access to computers and the facility or facilities in which they are housed, while ensuring properly authorized access is allowed.
- Password protection for all computers and portable devices
- Policies to secure PHI with specific controls such as strong passwords, email encryption, intrusion prevention software, locking down USB ports, etc.
- Policies to protect the facility and equipment from unauthorized physical access, tampering, and theft.
- Physical safeguards for all workstations that access PHI to restrict access to authorized users.
- Procedures to create and maintain retrievable exact copies of EPHI.
- Policies for guarding against and detecting malicious software.
- Measures to report and address security incidents.
- Policies and procedures for responding to an emergency or other occurrence, such as fire, vandalism, system failure, or natural disaster that harms systems that contain PHI.
- Device and media controls for the receipt and removal of hardware and electronic media that contain PHI into and out of a facility, and the transfer of these items within the facility.
- Technical security measures to guard against unauthorized access to PHI being transmitted over the internet.
- Confidential patient information whenever appropriate.
Employee Training
Employees need to sign confidentiality agreements and be educated on the following:
- Overall policies and practices to protect the security of electronic PHI in accordance with HIPAA rules
- Responsibilities in protecting PHI, identifying HIPAA violations, handling sensitive data, password security, threat recognition, breach prevention strategies, and necessary documentation for mitigating breaches
- Avoiding violations in social media use, public discussions of patient information, and accessing data on personal devices
- Importance of regular annual training to keep up-to-date with the latest requirements
It is also essential to maintain documentation clearly listing the roles and responsibilities of all staff involved. HIPAA documentation provides evidence of the security measures taken to protect the confidentiality of patient information.
Audits
In addition to strictly implementing HIPAA confidentiality agreements, reliable medical transcription companies conduct annual audits to assess their administrative, technical, and physical measures. This helps identify potential vulnerabilities that can compromise the integrity and confidentiality of PHI. Measures can then be taken to minimize the risks.
HIPAA Compliant Medical Transcription: Safeguard Against Breaches
Earlier this year, a cyberattack on a U.S. medical transcription service resulted in the theft of highly sensitive personal and health information from nearly nine million patients, marking one of the most severe medical data breaches in recent history (TedCrunch).
What are the consequences of such breaches?
The stolen data poses a range of risks, including personal distress, identity theft, and reputational damage for affected individuals. Additionally, cybercriminals can exploit compromised accounts to breach enterprise networks, causing potential corporate harm.
For healthcare organizations, such breaches lead to severe consequences. Beyond reputation damage, they face substantial financial losses due to investigative expenses and potential legal repercussions.
Maintaining patient privacy and confidentiality is a matter of medical ethics, fostering trust between patients, healthcare providers, and transcription companies, all of which is fundamental for quality care.
Healthcare providers need to their research well and choose a US based medical transcription services that can provide accurate and timely EHR documentation, and also ensure the confidentiality of PHI with strict measures for HIPAA compliance.