Table of Contents
Emergency Department (ED) documentation refers to the comprehensive records and notes created during a patient’s visit to the emergency room. These documents capture vital information about the patient’s medical history, symptoms, physical examination findings, diagnostic tests performed, treatments administered, medications prescribed, and any follow-up instructions given. ED documentation is unique because it is the only account of a patient’s ED visit and is completed under strict time constraints. As charting takes away from focus on patient care, physicians usually rely on emergency room transcription services to ensure accurate, detailed and timely capture of the patient encounter. Accurate documentation is crucial for continuity of care, ensuring accurate communication among healthcare providers, and to serve as a reference for future medical treatment or legal purposes.
If you didn’t document it, then you didn’t do it.
Importance of Accurate and Timely ED Charting
ED documentation provides a detailed account of the patient’s condition and the care provided during their emergency visit.
Accurate and timely ED charting is essential for proper communication. To provide the best patient care, healthcare providers who see the patient later need complete and accurate information about what was done in the ED. A report from www.saem.org notes: “Our chart is the main way we communicate with other health care clinicians (and even with patients) about what happened in the ED (e.g., diagnostics, treatments, our thought processes, discussions with patients and families about their concerns and desires, discussions with consultants about their recommendations and patient care plans)”.
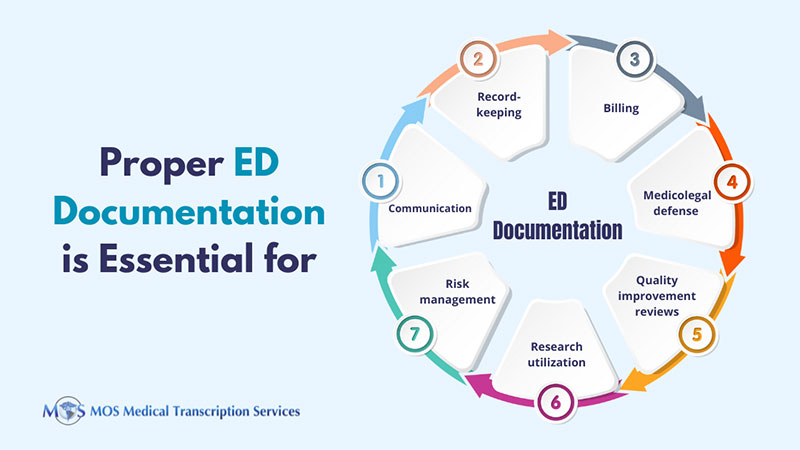
Some other reasons why proper ED charting is crucial are:
- Official record – The ED chart is the official record of the physician-patient encounter, H&P, and diagnostic and treatment plans.
- Billing – The nature of the actions performed in the ER should be clearly documented to justify the level of billing reported.
- Medicolegal defense – The chart should prove adherence to a high standard of care to serve as a defense in the event of a malpractice suit.
Good, clear ED charting is also critical for quality improvement reviews, research and utilization/risk management.
ED Documentation Requirements
There are several reasons why ED charting is unique and distinct from other physician notes. The ED note is a stand-alone completed under tight time pressures. The physician needs to focus on being brief while conveying as much information as possible for present and future care. Though the medical decision-making process is based on limited information, the chart should show all differential diagnoses.
The ED note should include everything that is relevant to the patient’s complaint including the subjective, objective, assessment and plan (SOAP) portions. Here are the four key elements that the ED note should contain as listed by the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
- Subjective Portion
The subjective section should cover:
- The patient’s presenting/chief complaint or the reason why the patient is medical care as stated by the patient.
- The history of present illness (HPI) – the main aspects of a symptom of the chief compliant (like pain): onset, location, quality, severity, timing/frequency, alleviating factors, and aggravating factors (OPQRST).
To avoid note bloat, the American College of Emergency Physicians instructs that documenting or importing the patient’s entire past, family and social history from prior medical records is necessary only when they are clinically relevant to the current evaluation and management service.
- Over-the-counter and prescriptions medications, and any medication allergies.
For patients with more chronic problems – compliance with any medications or medication side effects, current symptoms or complications, end organ effects, and any health care needs related to the chronic illness.
- Objective Section
The adage: “if you didn’t document it, then you didn’t do it” applies to this section.
- Include everything observed or measured during the interaction with the patient.
- Use standard medical language or commonly accepted abbreviations to report vital signs, general appearance, the relevant physical examination, and any laboratory or imaging results.
- Thorough physical examination documentation
- Results of any laboratory or radiologic studies ordered during the visit
- Assessment Section
The medical decision-making process is recorded in this section. Documentation comprises the following:
- Summary Statement – concise summary of the chief complaint along with main elements of the subjective and objective sections
- Problem List – details of all problems
- Discussion of Differential Diagnosis – brief account of a probable differential diagnosis for each acute problem on the problem list
- Plan Section
Each section of plan of action for the patient should be based in three things:
- Diagnostic recommendations – observation, laboratory tests, radiologic imaging, ECGs, or other diagnostic procedures
- Treatment options – medications and therapeutic procedures
- Follow-up plans – clear follow-up plan for future care
Role of Emergency Room Transcription Services
Emergency medicine practice involves multitasking to deal with complex clinical problems. Accurate, timely and detailed ED documentation is essential to show all differential diagnosis, high-risk conditions, and medical decision making. However, template-based software can often lead to inaccuracies and errors in the physician’s narrative. The solution is to add free text using dynamic templates, dictation, and medical transcription.
In 2017, the American Medical Association (AMA) reported on a study published in the Annals of Emergency Medicine that analyzed the effectiveness of electronic documentation in the ED. The lead author Joshua Feblowitz, MD noted: “The emergency department is a fluid and highly dynamic environment, with high volume, sick patients and frequent distractions and interruptions. The implementation of EHRs holds great promise in the emergency setting, but the environment is especially susceptible to changes that influence efficiency”.
The AMA report referenced Dr. Feblowitz, an emergency medicine resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital as saying that adopting new workflow strategies and technologies can improve the efficiency of documentation in the emergency department. According to Dr. Feblowitz, the use of scribes and electronic dictation software are two specific interventions that have the potential to improve completeness and efficiency of documentation.
By capturing all aspects of differential diagnosis and medical decision making, an experienced emergency medical transcription service provider can help ED physicians ensure thorough and accurate ED documentation as they focus on providing the best patient care.
Importance of Proper Documentation in ED Reports
Essential Components of ED reports
- Patient demographics
- Chief complaint
- History of present illness
- Vital signs
- Physical exam findings
- Lab results and imaging studies
- Diagnoses
- Treatments provided
- Discharge instructions
Benefits of Medical Transcription Services for ED Documentation
- Accurate, timely and thorough documentation
- Promotes high-quality patient care
- Facilitates communication among healthcare professionals
- Supports billing and reimbursement
- Ensures legal compliance.