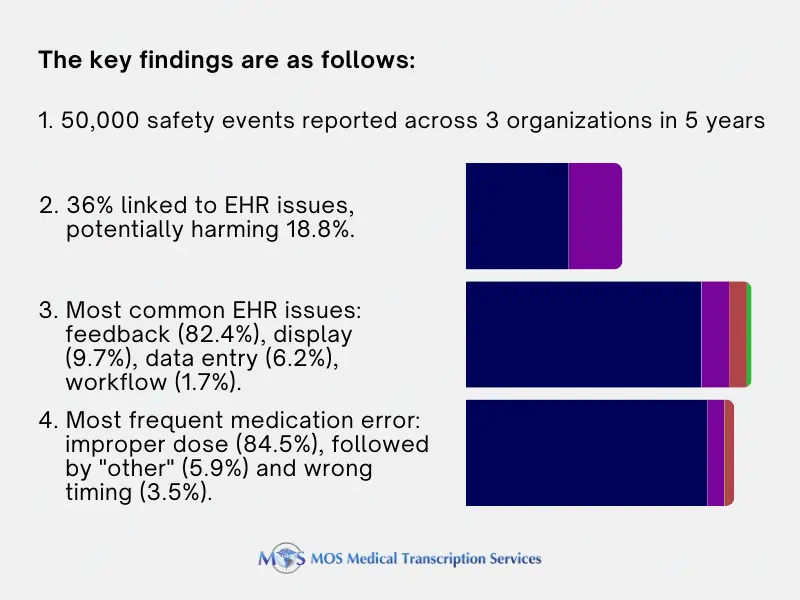
The innovative system of blending EHR and medical transcription service has helped medical professionals to achieve a higher level of quality in their work. Electronic Health Record or EHR is a systemized collection of patients’ healthrecords that are stored in electronic format. The EHR enhances the ability to exchange health data electronically and ensure high quality service and safe care for patients. EHR documentation includes complete details of the patient which includes name, data, demographics, allergies, medical history, medication, lab test reports, medical bills etc. These health records can be shared through a connected network across various health care settings so that providers can access the data from anywhere and give their expert opinion. The EHR market is expected to grow drastically by 2023. In many countries financial incentives are given for the implementation of EHR. The global electronic health record was valued at $23,592 million in 2016 and is expected to reach $33, 294 million by 2023.

Even though the EHR system provides various advantages, physicians are forced to sit in front of the computer rather than spend time with the patients.
The Centre for Medicare and Medicaid Services are aiming at reducing the burden of paperwork on physicians. Obtaining patient history and completing the documentation on a patient is very important from the point of view of patient care and good clinicians achieve that. Documentation should not be a burden because it is an integral part of patient care. However, documenting and re-documenting is a waste of time. Physicians should ensure that they are not wasting their valuable time by obtaining worthless information that may not be relevant to the care plan. One way to eliminate obtaining valueless information is to stop mandating arbitrary family history and random review of systems.
Here are some suggestions that Dr. Erica E Remer, a qualified and experienced Emergency Medicine physician with over 25 years of experience proposes whereby physicians can obtain valuable information, avoid useless information, and reduce the burden of medical documentation on healthcare providers.
-
- History is important it must be obtained by ancillary personnel and reviewed and validated by the provider. Stop copy and paste of previous documentation in prior notes.
- Family history and pertinent past medical or surgical history should be obtained.
- Social history of patients which may include tobacco or alcohol use should be collected as it may be relevant.
- The physical examination should be appropriate for the chief complaints or chronic condition or potential diagnoses.
- Medical decision making should clearly show what the provider was considering and thinking, the plan to evaluate the problems, and what the investigative studies demonstrated.
- Review of systems should be obtained and there should not be any numerical value of system so that patient cannot understand the seriousness of the illness.
- All diagnoses should be addressed.
- Medical necessity mustbe met for everyone.
- Submission of bill for payment should be on the basis of:
- Complexity of medical decision making like acute problems or multiple problems or high risk patients
- Time: complex history acquisition, review of various diagnostics studies, complex counselling, spending extra time talking to patients in case of unnecessary antibiotic or suicide and should be compensated, consultation and discussion with other healthcare providers.
- History is important it must be obtained by ancillary personnel and reviewed and validated by the provider. Stop copy and paste of previous documentation in prior notes.
Healthcare providers should be paid for the amount of work they have done. While documentation is important, giving proper patient care is more crucial. Healthcare units can minimize the burden of medical documentation by hiring a reliable medical transcription company that can ensure complete accuracy in the medical records. With good medical records and reliable health information healthcare centres can make better clinical decisions and also provide improved health care.