Table of Contents
The electronic health record (EHR) offers many advantages and have made documentation and provision of care easier for healthcare providers. As of 2021, nearly 4 in 5 office-based physicians (78%) and nearly all non-federal acute care hospitals (96%) had implemented a certified EHR, according to HealthIT.gov. EHR adoption has also increased in all specialties and many providers rely on outsourced medical transcription services to manage their documentation. The use of EHRs and medical scribes is an effective way to boost workflow and efficiency in the modern allergy and immunology clinic, according to a study published in Current Allergy and Asthma Reports in 2020.
Advantages of EHRs for Allergy Practices
The EHR system provides multiple benefits for allergy practices:
- Offers a centralized storage location for patient health information in legible format
- Provides quick access to patient records from anywhere, including remote locations
- Ensures immediate and easy access to patients’ allergy history, medication usage, and treatment plans
- Streamlines record-keeping processes
- Interfaces with labs, registries, and other EHRs
- Enables enhanced, rapid, effective communication
- Reduces risk of medication errors and duplicate information
- Improves care quality with enhanced decision support, clinical alerts, reminders, and medical information
- Improves compliance in immunizations
- Reduces costs and saves time searching for patient charts
The study authors noted that accurate and complete EHR documentation leads to improved patient charge capture and reduces billing errors. They also listed EHRs’ Allergy/Immunology specific attributes – recording allergy skin testing documentation; immunotherapy dose customization; administration, and documentation; incorporation of extract ordering, interface with pulmonary function testing and integrating questionnaires such as asthma control tests.
In addition to supporting providers, the EHR also provides many advantages for patients. The system facilitates appointment scheduling, reduces the need to fill out the same forms at each office visit, and sends notifications to providers about point-of-care data and important health interventions. E-prescriptions are electronically sent to the pharmacy. Patients can use the system’s patient portal to communicate with providers and receive electronic referrals for follow-up care with specialists.
However, despite their many benefits, in practice, EHRs can be time consuming to use on a daily basis. Providers point out that patient interaction can suffer when they perform EHR data entry during consults. EHRs also contribute to physician burnout.
Struggling with EHR data entry? Save time and focus on your patients with our customized medical transcription services.
Call (800) 670-2809.
Study: Scribe Support can Ease EHR Documentation
According to the study authors, implementing various strategies to support EHR use can help allergy practices streamline workflow, improve job satisfaction, and reduce physician burnout. The study provided evidence to show that scribe support can significantly improve documentation and workflow efficiency in medical practices:
Reduces patient visit duration: A 2018 oncology study found that when physicians were provided scribe support in the clinical setting, there was a 12.1% decrease in the overall patient visit duration compared to previous clinic visits without scribes.
Increases productivity and reduces costs per patient: A large outpatient urology office 2017 study reported that productivity (measures as both office evaluation and management visits and total relative value units) significantly improved by bringing in scribes. Another comprehensive study of emergency physicians reported that presence of scribes was associated with productivity gains, as measured by the mean number of patients per hour per physician. Making use of a scribe was also associated with reduced length of patient stay and costs per patient.
Promotes optimal use of office staff and reduces physician stress: Research suggests that addition of scribes can promote optimal use of office staff and proper delegation, and improve job satisfaction, and reduce physician burnout.
Methods for integrating Scribes into Practice
Scribes can participate in the clinical setting in different ways:
- Taking additional history before the provider sees the patient
- Annotating/transcribing medical notes in the room with provider
- Inserting the provider’s template note into the medical note (not in the patient’s room)
- Inserting the provider’s dictated note into the medical note (as done by medical transcription outsourcing companies)
- Using voice recognition
Allergists can choose the scribe integration method they are comfortable with based on the needs of their practice and their patients. While some physicians want to actively participate in the documentation process, many others prefer outsourcing medical transcription where the scribe takes on as much responsibility as possible to create accurate and timely EHR documentation. In fact, outsourcing comes with distinct advantages for busy allergists:
- Accuracy: Experienced medical transcription service providers employ trained transcriptionists who are knowledgeable about medical terminology and allergy-specific information and can ensure a high accuracy rate of 99%.
- Turnaround time: Quick turnaround time is crucial to ensure timely treatment and care for patients. By partnering with an expert, allergy practices can enjoy a TAT of 24 hours or less.
- HIPAA compliance: Allergy practices should make sure to choose a HIPAA complaint transcription service that has proper security protocols in place to protect patient information.
- Customized solutions: A reliable medical transcription company will adapt to allergy-specific templates and workflows to customize their services to meet the unique needs of allergy practices.
- EHR integration: By seamlessly integrating with the allergy practice’s EHR system, a medical transcription service provider can ensure easy transfer of transcribed information.
- Cost: Costs of allergy and sleep medicine transcription services can vary. Allergists can compare services and costs and choose the company that can provide value for money.
With the large number of service providers out there, choosing the right medical transcription company in the US can be a challenge. Allergists should carefully evaluate their requirements and make sure that the company they choose can provide accurate and timely allergy documentation solutions that meet their unique needs.

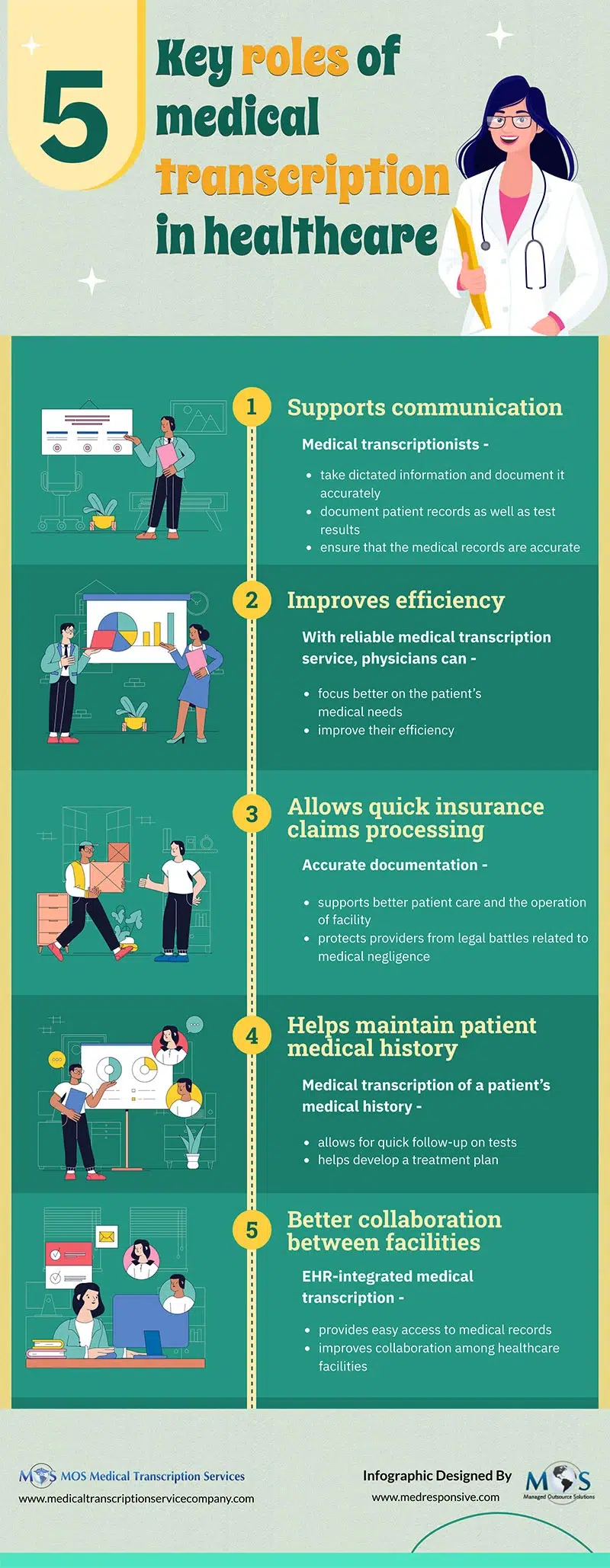



 Clear, accurate and timely medical records are essential to support patient care. Physicians need to relay precise and accurate data to the other members of the patient’s care team. Dictated reports are usually sent to a third party for transcription. One problem that teams in
Clear, accurate and timely medical records are essential to support patient care. Physicians need to relay precise and accurate data to the other members of the patient’s care team. Dictated reports are usually sent to a third party for transcription. One problem that teams in  According to ICD Coding Guidelines, all conditions co-existing at the time of the encounter that require or affect patient care and management must be clearly documented and assigned a diagnosis code. Each diagnosis must be documented clearly and precisely by the physician based on the clinical documentation from the face-to-face patient encounter.
According to ICD Coding Guidelines, all conditions co-existing at the time of the encounter that require or affect patient care and management must be clearly documented and assigned a diagnosis code. Each diagnosis must be documented clearly and precisely by the physician based on the clinical documentation from the face-to-face patient encounter.  For successful treatment of burns, adequate documentation is a major concern. Up-to-date burn injury documentation brings more challenges and requirements for practices. Emergency departments can consider
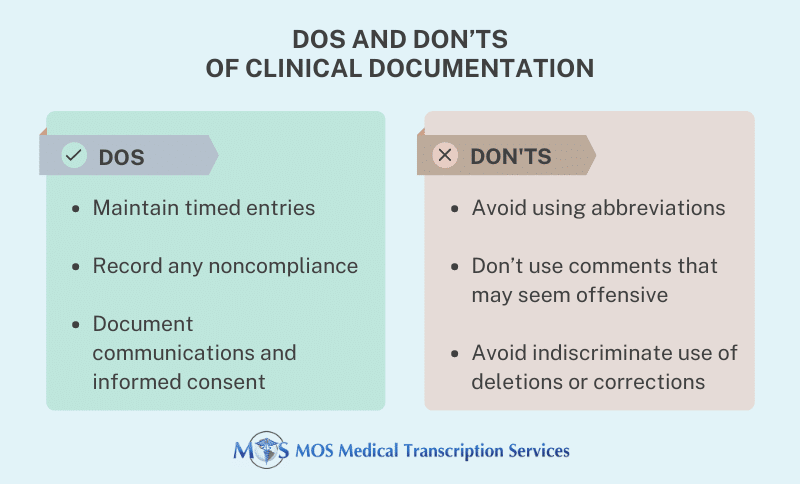
For successful treatment of burns, adequate documentation is a major concern. Up-to-date burn injury documentation brings more challenges and requirements for practices. Emergency departments can consider  Well-maintained clinical records are critical for practices to deliver quality healthcare, to maintain continuity of care, and to share information among different healthcare providers. Medical records must be accurate, and written in a professional manner. Records should also include diverse components including history, patient examination, differential diagnosis, treatment, follow-up, and progress.
Well-maintained clinical records are critical for practices to deliver quality healthcare, to maintain continuity of care, and to share information among different healthcare providers. Medical records must be accurate, and written in a professional manner. Records should also include diverse components including history, patient examination, differential diagnosis, treatment, follow-up, and progress.