Table of Contents
In an era where healthcare relies heavily on digital tools, automated medical transcription security has become one of the most crucial concerns for providers, patients, and technology partners alike. As more practices adopt advanced medical transcription services to streamline documentation and reduce administrative burden, the need to safeguard sensitive health information has never been greater. From AI-driven transcription tools to cloud-based storage systems, every digital touchpoint presents both an opportunity for efficiency and a potential gateway for risk.
Understanding how privacy, data protection, compliance frameworks, and modern encryption methods work together is essential to ensure safe, accurate, and trustworthy documentation. In this post, we dive deep into everything you need to know about privacy and security in automated medical transcription, so you can embrace innovation without compromising patient confidentiality or organizational integrity.
Understanding Automated Medical Transcription Security
Automated transcription services use artificial intelligence (AI) to convert spoken audio into written text. In healthcare, these systems help providers document patient encounters, record clinical conversations, and enhance the accuracy of electronic health records (EHRs). Many organizations now rely on AI-powered medical transcription for several reasons:
- Save time on manual charting
- Make clinical conversations searchable
- Enhance telehealth documentation
- Improve recordkeeping compliance
- Improve efficiency of patient care
Since medical audio often contains diagnoses, medications, personal identifiers, and other confidential details, selecting a secure, trustworthy AI system is crucial. Most of the organizations handle sensitive information in their transcription workflows, highlighting the urgent need for strong healthcare data security practices.
The HIPAA Journal has tracked healthcare data breach statistics since October 2009, the month when the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR) began publicly posting summaries of reported breaches on its website. The latest update, published on October 27, 2025, reflects information submitted to OCR through October 20, 2025.
From 2009 to 2024, a total of 6,759 healthcare data breaches involving 500 or more patient records were reported. These incidents led to the exposure or unauthorized disclosure of protected health information affecting 846,962,011 individuals.
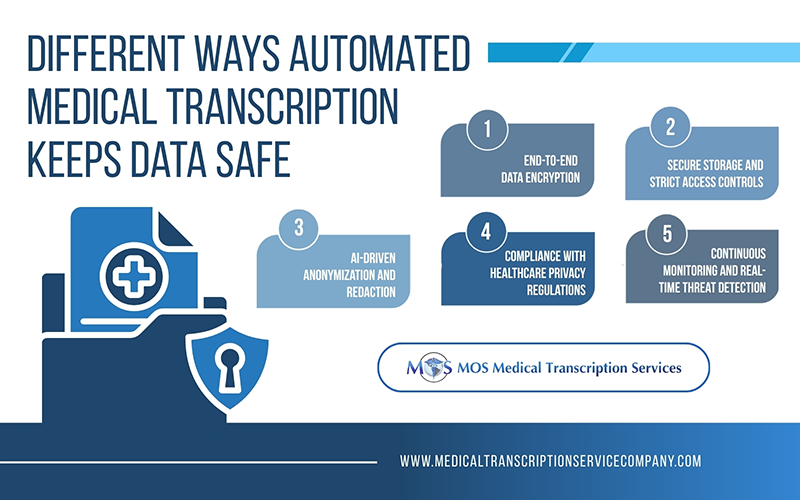
How Automated Medical Transcription Keeps Data Safe
Modern automated transcription platforms use multilayered protection to secure patient data and ensure regulatory compliance. Below are the most essential security features that reputable providers implement.
- End-to-End Data Encryption: Protecting Your Files at Every Step
The importance of encryption in automated medical transcription systems cannot be overstated. It transforms information into unreadable code that only authorized systems or individuals can access.
- Data in transit: When clinical audio files are uploaded, they are secured using SSL/TLS encryption, the same standard used by banks.
- Data at rest: Once stored, the files remain encrypted so no outsider—or even internal staff—can view them without proper clearance.
This dual-layer encryption prevents hackers, unauthorized staff, or external threats from intercepting or decoding sensitive patient details.
- Secure Storage and Strict Access Controls
High-quality transcription providers host data on secure servers located in highly controlled data centers equipped with:
- Biometric entry points
- Round-the-clock surveillance
- Firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Security-trained personnel
Many platforms also implement secure methods for storing medical audio and transcript files, ensuring only approved users can access them. Role-based access control further limits exposure by granting data access solely to authorized team members.
- AI-driven Anonymization and Redaction
Advanced systems can automatically hide or remove sensitive identifiers such as:
- Patient names
- Phone numbers
- Addresses
- Medical record numbers
- Social security numbers
This helps maintain secure clinical documentation even when files are used for research, training, or case analysis. Automated anonymization significantly reduces the risk of privacy breaches if data is leaked, shared, or accessed unintentionally.
- Compliance with Healthcare Privacy Regulations
Any medical transcription system must comply with global and industry-specific privacy frameworks such as:
- HIPAA (for U.S. healthcare organizations)
- GDPR (for European patient data)
- ISO 27001 (international security standard)
- HITECH Act
These frameworks require service providers to uphold strict data-handling practices, conduct regular audits, implement breach reporting systems, and maintain transparency. A provider committed to compliance demonstrates reliability and a strong dedication to patient protection.
- Continuous Monitoring and Real-time Threat Detection
Modern cybersecurity threats evolve quickly, making real-time monitoring essential. Automated and manual systems work together to track unusual events such as:
- Suspicious logins
- Irregular download patterns
- Unauthorized access attempts
- System vulnerabilities
When issues arise, security teams can respond immediately—minimizing risks and preventing data loss. Regular software updates help patch weaknesses and keep platforms protected against emerging threats.
How AI-enabled Medical Transcription Services Ensure Privacy and Safety
AI does more than speed up transcription, it enhances security in ways traditional workflows cannot.
- Reduced Human Handling of Data: AI transcription minimizes manual involvement, meaning fewer people access patient information. This significantly lowers the risk of accidental or intentional data leaks.
- Automated Redaction and Smart Detection: AI algorithms can recognize sensitive details and redact them instantly, enhancing compliance and ensuring safer document usage across teams.
- Intelligent Threat Detection: AI-powered monitoring systems can detect inconsistencies or unusual behavior in real time, offering a more robust layer of protection.
- Improved Accuracy and Contextual Understanding: As AI systems are trained on vast amounts of medical terminology, they produce more accurate transcripts, reducing errors that can threaten patient safety or lead to misinformation.
This combination of speed, accuracy, and built-in safeguards makes AI-enabled solutions one of the most secure choices for healthcare organizations today.
What Users Can Do to Enhance Security
Even the most secure transcription system needs user cooperation to maintain protection. Healthcare professionals should:
- Use strong, unique passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Avoid sharing login credentials
- Keep systems updated
- Delete files after downloading transcripts
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi for uploads
These simple actions add important layers of safety.
As digital healthcare expands, protecting patient information has become most important. Organizations can confidently use AI-powered medical transcription services that utilize strong automated medical transcription security protocols such as encryption, secure storage, and continuous monitoring. When combined with user responsibility and the right provider, automated transcription becomes a powerful and safe tool for modernizing clinical workflows.
Healthcare continues to evolve, and secure AI-driven documentation is key to enhancing patient trust and operational efficiency.