Accurate medical reports enable medical professionals to improve patient care and enhance healthcare industry standards. Precise cardiac arrest documentation is essential for recording and monitoring cardiopulmonary resuscitation events and outcome data. It also helps to be clear when comprehending and communicating important information for additional care. Gathering information on in-hospital cardiac arrest resuscitation is useful in terms of legal, quality control, scientific, and patient interests. The quality and efficiency of medical documentation can be considerably improved by using medical transcription services, which guarantee that every relevant detail is accurately recorded. Cardiologists and their teams can focus on delivering top-notch patient care while utilizing adaptable dictation systems to record their observations, treatment outcomes, progress notes, and so on which can then be efficiently transcribed using cardiology transcription.
Table of Contents
Importance of Accurate Cardiac Arrest Documentation
Cardiac arrest is one of the most critical events in a healthcare context, requiring prompt, coordinated, and standardized actions in order to produce a favorable outcome. Given that healthcare professionals are responsible for determining a patient’s state for resuscitation, it may be presumed that the majority of cardiac arrest calls are due to unplanned or undesirable complications of the illness or medical care being provided, that may sometimes fail to treat the cardiac arrest.
In these situations, irrespective of a primary medical duty to audit results and processes, scrutiny of procedure can be anticipated under critical event analysis, complaints, legal proceedings, or, even police or health and safety executive investigations. In these situations, accurate cardiac arrest documentation is essential. If the patient survives, thorough documenting of earlier occasions, timeframes, and procedures is essential for improving or organizing subsequent care.
If any section of the records is missing or unreadable, information about the in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) may be lacking or erroneous. There are three crucial purposes for the patient record created during a code blue:
- The record acts as a guide for post-event treatment and as a real-time patient management tool during the event.
- The gathered data is a valuable resource for guiding initiatives aimed at improving quality.
- If gathered correctly, the record is the single best picture for recreating the event if risk management difficulties occur.
Check out the infographic below
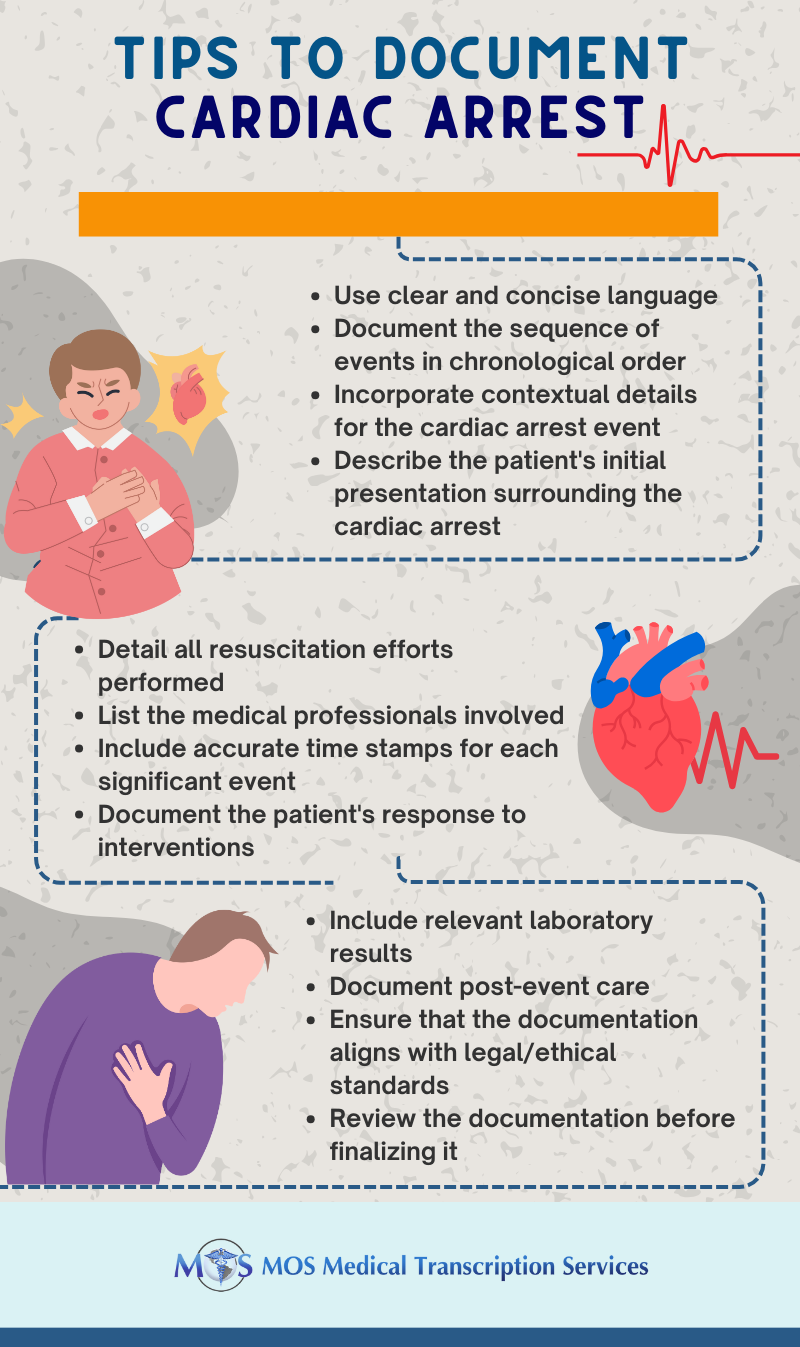
4 Essential Cardiac Arrest Documentation Tips
Patients who are in cardiac arrest pose some of the most difficult patient care circumstances. The following pointers for improving cardiac arrest patient documentation came from Steve Krantz, a paramedic with 35 years of experience working as a medic and EMS educator in Wisconsin. All of the CPR patient documentation for Krantz’s service underwent quality assurance. So, here are the four tips.
- Any interventions made by onlookers before EMS arrives should be documented: Find out whether and when the bystanders started CPR. Likewise, try to figure out whether the bystanders merely performed compressions or if they also administered rescue breaths. Understanding bystander engagement can help in directing public education campaigns and explaining why interventions like defibrillation may or may not have been successful.
- Verify the patient’s status as it was last heard or seen: Find out whether the patient’s spouse checked straight away or waited until she was done with what she was doing before discovering the patient in cardiac arrest if she claims to have heard a thump in the other room.
- Obtain the patient’s medical history information: This is crucial for patients who are being transferred or for whom field resuscitation is under consideration. Diabetes, kidney illness, cancer, or another medical condition could have made resuscitation more difficult or led to the arrest.
- Capture of the field’s end time: Record the time the last compression was performed if the local procedure permits ending resuscitation efforts. The time at which resuscitation efforts were actually completed was probably far earlier than when the health professionals left the scene.
Some Other Tips for Cardiac Arrest Documentation
Here are some other basic documentation tips for managing cardiac arrest cases effectively:
- Start with basic patient information: Patient identification includes the patient’s full name, date of birth, and medical record number. This core information guarantees that the documentation is assigned to the correct patient. Make a note of the precise time and date when the cardiac arrest was initially identified and the code was called. Accurate time stamping is critical for understanding the order of occurrences.
- Document the initial assessment: Describe the patient’s state when discovered, including his/her level of consciousness, the presence of a pulse, and any indications of distress. Clear descriptions aid in comprehending the patient’s baseline condition. Note if the cardiac arrest was witnessed or unwitnessed, as this influences the resuscitation strategy and probable consequences.
- Keep a record of the resuscitation efforts: Note the person who started CPR, when it was started, and the effectiveness of the compressions. Provide information regarding the depth, pace, and any compression pauses. Note how many shocks were given, how much energy was consumed, and how the patient reacted to each shock. Keep track of the time of each attempt at defibrillation and any variations in rhythm. Make a list of all the drugs administered during the resuscitation, together with their dosages, routes of administration, and timings.
- Keep track of and document vital signs: Maintain a regular record of the patient’s vital indicators, such as blood pressure, oxygen saturation, heart rate, and breathing rate. Regular updates guarantee an ongoing log of the patient’s condition.
- Teamwork and Communication: Record the duties and activities of every team member participating in the resuscitation. This includes the person who used the defibrillator, gave the medication, and performed CPR. Note important decisions and conversations that occurred during the resuscitation. Successful teamwork and coordinated efforts depend on effective communication.
- Outcome and Post-resuscitation Care: If ROSC (Return of Spontaneous Circulation) is achieved, note the care given and the patient’s following status and vital signs. Document airway management, ventilation assistance, and, if necessary, the transition to higher care levels.
Maintain accurate, legible records that clearly reflect the essential clinical findings, decisions taken, information provided to patients, and any prescription medicines or other investigations or treatments that were carried out. Record-keeping must be done either simultaneously with the recording of occurrences or as soon as possible afterwards. This is when a cardiology transcription service may prove highly supportive. To meet their transcription needs, cardiologists require excellent accuracy, quick turnaround, and a dynamic workforce.
Cardiologists can dictate while concentrating on giving the patient the best care with the flexible dictation systems and delivery options of medical data available. With the use of smartphone apps, digital recorders, and toll-free phone dictation, dictating medical notes has become rapid and simple. Oral notes can then be typed, checked for inaccuracies, and swiftly converted into transcripts or medical records. Using medical transcription eliminates the need to understand handwritten notes or look for misplaced documents. For health care providers like cardiologists, nurses and others, having extra time to spend with patients is undoubtedly beneficial.
Doctors can enhance the standard of patient care by outsourcing their cardiology medical transcription needs. Medical organizations can lighten their effort and concentrate more on patients by not having to worry about recording activities or entering data. Also, by just providing a voice recording, clinicians can have access to accurate medical documentation. Medical staff might not be able to provide the necessary clarity and accuracy in documentation due to the busy schedule at the hospital. They might make mistakes when deciphering words, which would result in inaccurate documentation whereas qualified experts of medical transcription services for cardiology guarantee accuracy in every file they transcribe, and prepare reliable cardiac arrest documentation. They follow HIPAA regulations, which ensures that medical practitioners are not exposed to any legal risk.
![Radiology Transcription Challenges Practices Face [INFOGRAPHIC]](https://www.medicaltranscriptionservicecompany.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/radiology-transcription-challenges-practices-face.webp)
![Medical Record Documentation Requirements For Podiatry [INFOGRAPHIC]](https://www.medicaltranscriptionservicecompany.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/medical-record-documentation-requirements-for-podiatry.jpg)
![Advantages of Real-Time Data Entry for Medical Reporting [INFOGRAPHIC]](https://www.medicaltranscriptionservicecompany.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/advantages-real-time-data-entry-for-medical-reporting.jpg)